1. Introduction
The term carbon steel pipe (cs pipe)can be used to describe various tubular metal products whose main alloying element is 0.12%-2% carbon. In addition to carbon, elements such as chromium, cobalt, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, titanium, and tungsten can be added, as well as vanadium and zirconium, to achieve specific alloying effects. For example, A333 Grade 6 pipe has high tensile strength and impact properties in low-temperature applications compared to A106 Grade B pipe, which is used at room temperature or higher. This is achieved by adding more than 0.9% manganese, which is limited to 0.65% in A106 pipe.
Carbon steel pipe is a type of steel pipe manufactured primarily from carbon steel, with a carbon content typically in the low to medium range. It is formed through processes such as hot rolling, cold drawing,
ERW , or
seamless manufacturing. It features high strength, low cost, and good machinability, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including the transportation of fluids such as water, oil, and gas, as well as structural support, mechanical processing, and construction projects. Therefore, it is one of the most commonly used and cost-effective steel pipes in industrial and engineering projects.

2. Composition and Properties of Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is primarily composed of iron (Fe) and carbon (C), with a carbon content generally ranging from 0.02% to 2.1%. It may contain small amounts of elements such as manganese (Mn), silicon (Si), sulfur (S), and phosphorus (P), but these elements are not added for specific performance characteristics; they are considered ordinary impurities or trace alloying elements. Based on carbon content, carbon steel can be classified into:
Low-carbon steel (≤0.25% C)
Medium-carbon steel (0.25%–0.6% C)
High-carbon steel (0.6%–2.1% C)
High-quality carbon structural steel is purer, contains fewer impurities, and has better mechanical properties. It can be heat-treated as needed. Low-carbon (≤0.25%) high-quality steel is often used for carburized parts, such as gears and shafts; medium-carbon (0.25%–0.60%) steel, such as 40 and 45 steel, is often heat-treated and used for mechanical parts; high-carbon (>0.60%) steel, such as 65Mn, is used to manufacture components that require high load-bearing capacity and wear resistance, such as springs. Overall, ordinary carbon steel prioritizes cost-effectiveness, while high-quality carbon steel offers higher performance and a wider range of mechanical applications.
3. Manufacturing Process of Carbon Steel Pipes
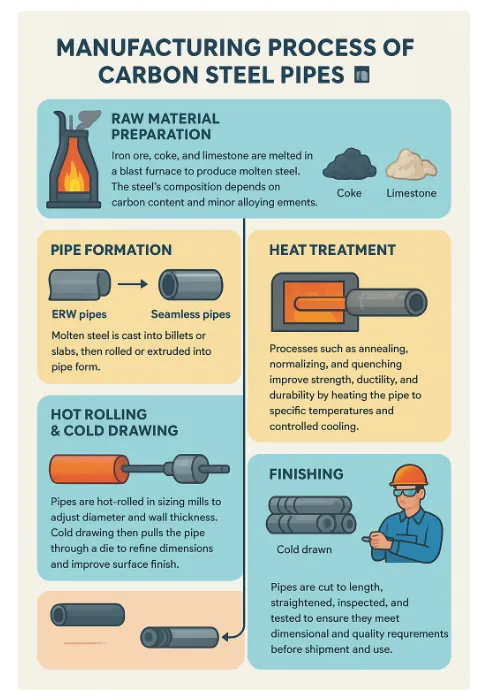 4. Types of Carbon Steel Pipes
4. Types of Carbon Steel Pipes
Carbon steel pipes can be classified according to manufacturing process into seamless steel pipes (high pressure resistance and good sealing performance), welded steel pipes (straight seam ERW, submerged arc welded SAW), and cold-drawn/cold-rolled pipes (high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface). They can also be classified by shape into round pipes, square/rectangular pipes, and special-shaped pipes. According to application, they can be classified as structural pipes, fluid pipes, mechanical pipes, boiler pipes, and line pipes. Finally, they can be classified by carbon content into low-carbon, medium-carbon, and high-carbon steel pipes.
Seamless pipes are commonly used in high-pressure boilers, oil and gas, and mechanical parts; welded pipes are suitable for medium and low-pressure transportation and large-diameter pipelines; square and rectangular pipes are mostly used in construction and furniture; cold-drawn pipes are used in machinery manufacturing and hydraulic systems; and high-carbon pipes are used for high-strength tools and parts.
According to carbon content, carbon steel pipes can be classified into low-carbon steel pipes (≤0.25% C), medium-carbon steel pipes (0.25–0.60% C), and high-carbon steel pipes (>0.60% C). This classification mainly reflects the strength, hardness, plasticity, and toughness of the steel pipes.
|
Category
|
Carbon Content
|
Main Characteristics
|
Typical Applications
|
Common Steel Grades Example
|
|
Low Carbon Steel
|
≤ 0.25%
|
Good plasticity, toughness, and weldability; relatively low strength
|
Fluid transport pipelines, building structures
|
10, 20
|
|
Medium Carbon Steel
|
0.25% - 0.60%
|
Higher strength and hardness, with some plasticity
|
Manufacturing mechanical parts (e.g., shafts, connecting rods)
|
30, 35, 45
|
|
High Carbon Steel
|
> 0.60%
|
High strength and hardness, but more brittle; lower plasticity
|
Tools, molds, and components requiring high hardness and wear resistance
|
High-carbon tool steel
|
In addition, depending on specific usage scenarios, carbon steel pipes can also be produced in many specialized types, such as medium- and low-pressure boiler pipes, high-pressure boiler pipes, petroleum cracking pipes, and geological exploration pipes. Each has corresponding national standards (e.g., GB/T 3087, GB 5310) to strictly regulate chemical composition and mechanical properties.
5. Applications of Carbon Steel Pipes
Carbon structural steel pipes have a wide range of applications and are suitable for various uses. Some of the most common applications of carbon steel pipes include:
Building foundations
Transporting natural gas or oil
Boiler and condenser tubes
Conveying wastewater
Chemical processing
High-pressure applications
Sewage transport
Column construction
Shipbuilding
Structural support
Garbage bins
Distillation columns
OEM applications
6. Advantages of Carbon Steel Pipes
Carbon steel pipes offer safety and durability. Their impact resistance and resilience to harsh environmental conditions such as pressure or extreme weather make them an ideal material for structural applications.
The incredible strength of carbon steel means that pipes can be made thinner, using less material, while still being able to transport large volumes. This makes carbon steel pipes a cost-effective material. Not only can less material be used, but carbon steel is also recyclable, making it both environmentally friendly and economical.
Carbon steel pipes are a versatile material due to their ease of manufacture. We at
baowi steel can produce products in various thicknesses and sizes. They are also easy to cut and bend to fit any need. They can also be easily connected to joints, valves, and other pipe fittings.
7. Will carbon steel rust?
Yes, carbon steel will rust. Carbon steel is mainly composed of iron and a small amount of carbon. Iron is prone to oxidation in humid or oxygen-containing environments, forming rust (iron oxide), which leads to surface corrosion and reduced strength. Therefore, carbon steel pipes usually require rust prevention treatment during use, such as galvanizing, painting, or applying anti-corrosion coatings, to extend their service life.
8.How does carbon content affect the properties of carbon steel?
Carbon steel, an alloy of iron and carbon (0.05%–2.0% carbon), has properties strongly influenced by its carbon content. Higher carbon increases hardness and strength but reduces ductility and toughness, making the steel more brittle. Lower carbon makes steel softer, more ductile, and easier to form, but less strong. Carbon content also affects machinability and corrosion resistance, so choosing the right level is key to meeting specific application requirements.
9.What are the common specifications of carbon steel pipes?
Carbon steel pipes come in a wide variety of specifications, with significant differences in their outer side length, ranging from just a few millimeters to hundreds of millimeters. For example, smaller specifications include 10mm, 12mm, and 14mm, while larger specifications include 108mm, 159mm, and 219mm. The wall thickness also varies, from as thin as 1mm to tens of millimeters. These different outer side lengths and wall thicknesses combine to create a wide variety of specifications to meet the needs of various projects.
10. Conclusion
In summary, carbon steel is a widely used material across various industries due to its unique properties. Differences in carbon content and other alloying elements result in different grades of carbon steel with varying properties and applications. Carbon steel differs from other types of steel because it is relatively inexpensive, easy to manufacture, and has high strength. Its high tensile strength, durability, and wear resistance make it suitable for construction, automotive, and manufacturing industries.
The carbon content of carbon steel plays a crucial role in determining its properties. Higher carbon content leads to higher hardness, strength, and wear resistance. However, excessive carbon content results in brittleness and reduced ductility. Carbon steel can be hardened through heat treatment, quenching, and tempering, making it suitable for cutting tools, springs, and other applications requiring high strength and wear resistance.
Although carbon steel has high corrosion resistance, it will rust when exposed to moisture and oxygen. This problem can be addressed by applying a protective coating to the surface or using corrosion-resistant alloys.








 English
English Español
Español بالعربية
بالعربية












 Phone :
Phone :  Whatsapp :
Whatsapp :  Email :
Email : 


