Tubular steel products are manufactured mainly by two different methods resulting in seamless pipes or in welded pipes. The starting material is always a hot steel billet. In the first case, the hot billet is processed by punching, hot rolling and stretch-reducing rolling into a seamless tube. In the second case, the hot billet is shaped into a plate or a strip by hot and cold rolling; the plate or strip is then bent and the edges are sealed by welding.
Introduction to the production process of hot-rolled steel pipes
Hot-rolled steel pipes are a very common steel pipe material. The production and manufacturing of steel pipes is a common steel pipe production process. Most of the steel pipes in our lives are made by hot rolling or cold pressing. Hot rolling is made at high temperature, and cold rolling is made at recrystallization temperature. The materials produced by these two production processes are different. Most steel pipes will use hot rolling technology, because hot rolling technology can not destroy the degree of crystallization of steel pipes. The following editor will introduce the process of hot-rolled steel pipes to you.
Hot-rolled steel pipe production process:
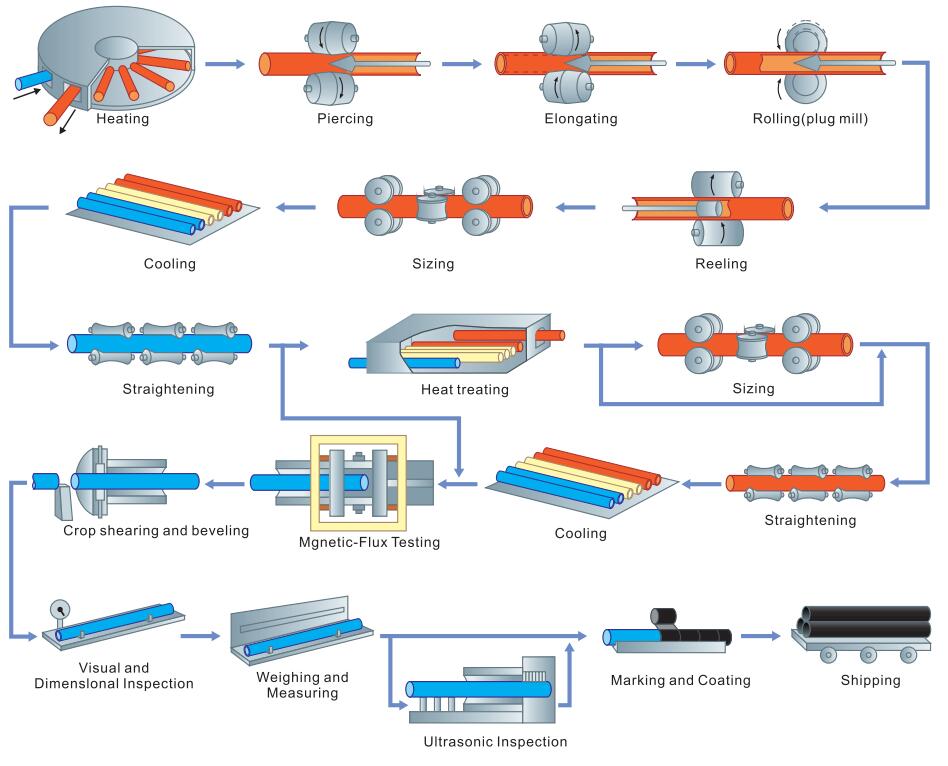
1. Main production process of hot-rolled seamless steel pipe (main inspection process) Steel pipe production and manufacturing: tube blank preparation and inspection → tube blank heating → perforation → tube rolling → steel pipe reheating → sizing (reducing) diameter → heat treatment → finished tube straightening → finishing → inspection (non-destructive, physical and chemical, bench inspection) → storage 2. Main production process of cold-rolled (drawn) seamless steel pipe: blank preparation → pickling and lubrication → cold rolling (drawing) → heat treatment → straightening → finishing → inspection The general production process of seamless steel pipe can be divided into cold drawing and hot rolling.
Cold-rolled seamless steel pipe
The production process of cold-rolled seamless steel pipe is generally more complicated than hot rolling. The tube blank must first be rolled with three rollers, and then the sizing test must be carried out after extrusion. If there is no response crack on the surface, the round tube must be cut by a cutting machine and cut into a blank with a length of about one meter. Then enter the annealing process. Annealing must be pickled with acidic liquid. During pickling, pay attention to whether there is a large amount of bubbles on the surface. If there is a large amount of bubbles, it means that the quality of the steel pipe does not meet the corresponding standards. In appearance, the cold-rolled seamless steel pipe is shorter than the hot-rolled seamless steel pipe. The wall thickness of the cold-rolled seamless steel pipe is generally smaller than that of the hot-rolled seamless steel pipe, but the surface looks brighter than the thick-walled seamless steel pipe, the surface is not too rough, and the diameter does not have too many burrs.
Production process of cold-rolled seamless steel pipe
After strict manual selection by the staff, the surface is oiled after quality inspection, followed by multiple cold drawing tests, and the perforation test is carried out after hot rolling. If the perforation diameter is too large, it must be straightened and corrected. After straightening, it is transferred to the flaw detector by the conveyor for flaw detection, and finally labeled, arranged in specifications, and placed in the warehouse. Round tube billet → heating → perforation → three-roller oblique rolling, continuous rolling or extrusion → tube removal → sizing (or reducing diameter) → cooling → straightening → hydraulic pressure test (or flaw detection) → marking → storage Seamless steel pipe is made of steel ingot or solid tube billet through perforation into rough tube, and then made by hot rolling, cold rolling or cold drawing. The specifications of seamless steel pipes are expressed in millimeters of outer diameter * wall thickness.
Comparison between hot-rolled seamless steel pipes and cold-rolled seamless steel pipes
The outer diameter of hot-rolled seamless pipes is generally greater than 32mm, and the wall thickness is 2.5-200mm. The outer diameter of cold-rolled seamless steel pipes can reach 6mm, the wall thickness can reach 0.25mm, and the outer diameter of thin-walled pipes can reach 5mm and the wall thickness is less than 0.25mm. Cold rolling has higher dimensional accuracy than hot rolling. Generally, seamless steel pipes are made of 10, 20, 30, 35, 45 high-quality carbon steels, 16Mn, 5MnV and other low-alloy structural steels, or 40Cr, 30CrMnSi, 45Mn2, 40MnB and other alloy steels, which are hot-rolled or cold-rolled. Seamless pipes made of low-carbon steels such as 10 and 20 are mainly used for fluid delivery pipelines. Seamless pipes made of medium-carbon steels such as 45 and 40Cr are used to manufacture mechanical parts, such as load-bearing parts of automobiles and tractors. Generally, seamless steel pipes must ensure strength and flattening tests. Hot-rolled steel pipes are delivered in hot-rolled or heat-treated state; cold-rolled steel pipes are delivered in heat-treated state.
The above is an introduction to the production process of hot-rolled steel pipes. Do you know what the production process of hot-rolled steel pipes is now?
Hot-rolled steel pipes are a kind of steel pipe that can resist oxidation. This kind of steel pipe has high toughness and is not easy to deform. Hot-rolled steel pipes are mainly used to make underground water pipes, and can also be used to make parts for some large machinery and equipment. It is a very common steel pipe material. Hot-rolled steel pipes are also used in most construction projects. Hot-rolled steel pipes have models and sizes. Everyone should pay attention when purchasing.
Steel pipe knowledge: How are seamless steel pipes made?
A production process for large-diameter alloy seamless steel pipes A production process for large-diameter alloy seamless steel pipes. It includes the following steps: step one, material preparation; step two, heating and oblique rolling and perforation of the tube billet; step three, rough tube trimming; step four, hot expansion deformation and sizing; step five, heat treatment; step six, straightening; step seven, internal grinding; step eight, deviation correction; step nine, external grinding; step ten, flaw detection and inspection; step eleven, re-finishing, final inspection and packaging. The present invention can not only produce high-grade alloy seamless steel pipes within a large group spacing range, but also has relatively small investment, high product quality, high production efficiency and low production cost. The main production process of seamless steel pipes is heating of tube billets and billets, perforation of tube billets, extension of steel pipes, rolling of steel pipes, sizing and reducing of steel pipes, cooling and finishing of steel pipes, or it can be said that heating of steel billets, perforation, hot rolling, pickling, cold drawing, carbon burning, head cutting, spraying, packaging and finished products. A method for manufacturing seamless steel pipes, characterized in that: a rolling mill stand having multiple rolling rollers and a mandrel-type seamless pipe rolling mill are arranged in succession in different rolling directions; after the seamless steel pipe is rolled on such a manufacturing production line, the wall thickness of the rolled steel pipe in the circumferential direction is measured at multiple points; based on the measurement results, at least the two end positions of each axis of the rolling rollers on the final rolling mill stand of the mandrel-type seamless pipe rolling mill are controlled separately to minimize the uneven wall thickness.
Production of welded steel pipes
Welded steel pipes are made using steel plates or coiled steel strips. In the first case, the plate is rolled into a round section with the help of a bending machine. Then, the adjoining edges are sealed together by longitudinal welding. In the second case, the strip is rolled into a circular section with the help of funnel rolls. Depending on the forming process, the strip is bent either along its longitudinal axis (and the edges are longitudinally welded) or in a helical form (and the edges are spirally welded).
There are two types of processes for the production of welded pipes: pressure welding and fusion welding. The most common pressure welding methods are the Fretz-Moon process, direct current electric resistance welding (ERW), low frequency (LF) electric resistance welding, high frequency (HF) induction welding, and high frequency (HF) conduction welding. In the ERW process, a pipe is manufactured by cold-forming a flat sheet of steel into a cylindrical profile. The two edges of the steel cylinder are heated through electrical current and sealed together without the use of welding filler material. The most common fusion welding processes are submerged arc welding (SAW), and gas shielded welding, such as MIG or TIG.
Tube drawing
Tube drawing is used to resize large diameter tubes into smaller ones. It is performed at room temperature by pulling the tube through a die. In some instances, the required size may not be obtained directly from the rolling mill, therefore cold drawing can be used. In this process, the tubes or pipes are coated with an oxalic and soap solution to reduce friction while drawing. The tube or pipe is pulled over a drawing bench using die plugs. The result is a high-quality tube with precise dimensions, good surface finish, and added strength. For such reasons, this process is widely employed in the metalworking industry. There are different tube drawing technologies. In many cases, a mandrel is used to prevent buckling or wrinkling in the tube.
Finishing
The rolled pipes and tubes are cut to the required lengths and cleaned. A heat treatment is performed to remove stresses that may occur during the previous forming and welding phases. After the heat treatment, the tubular products are pickled, descaled, and straightened. Moreover, they can be galvanized and marked for identification. Based on the final application, their ends can be threaded or beveled by machining. After a set of testing and quality checks, the tubes are finally ready for packing and shipping.








 English
English Español
Español بالعربية
بالعربية











 Phone :
Phone :  Whatsapp :
Whatsapp :  Email :
Email : 


