Definition of steelmaking: Using oxidation method to remove impurities from pig iron and scrap steel, adding appropriate amount of alloying elements to make it into steel with high strength, toughness or other special properties, this process is called "steelmaking".
Iron-carbon alloy with carbon content ≤2.0%, the meaning of 2.0%C in the iron-carbon phase diagram. High temperature: austenite, good hot working performance; room temperature: mainly pearlite.
Why steelmaking ?
Pig iron cannot be widely used. High carbon content: no austenite at high temperature; poor performance: hard and brittle, poor toughness, poor welding performance, cannot be processed; many impurities: high content of S, P, and inclusions.
Steelmaking process flow
Modern steelmaking processes use a high degree of automation and refining techniques to ensure high product quality. The following are the main process flows of steelmaking:
Desulfurization
The sulfur content in the molten iron is reduced through desulphurization stations.
Dephosphorization
Phosphorus impurities are removed in the dephosphorization converter to ensure the toughness and crack resistance of the steel.
decarbonization
Rapidly oxidize carbon elements in high-temperature converters to improve the purity and mechanical properties of steel.
Process characteristics
Use "all three desulfurization" technology (desulfurization, dephosphorization, decarbonization).
Efficient refining process and continuous casting technology ensure the cleanliness of molten steel and production efficiency.
Innovative steelmaking technology
1. Dephosphorization converter bottom blowing technology
By optimizing the bottom blow gun design and online replacement technology, the dephosphorization efficiency is improved and the phosphorus content in semi-steel is significantly reduced.
2. CO₂-O₂ mixed injection technology
Mixed injection of CO₂ and oxygen is used in the converter to improve the metallurgical effect, reduce TFe content and smoke emissions, and improve environmental performance.
3. Converter hypoxia control
Combined with the RH refining process, the oxygen content at the end of the converter is reduced, the cleanliness of the molten steel is improved, and the demand for high-quality steel production is met.
4. High-speed continuous casting technology
By optimizing the heat transfer and lubrication conditions of the crystallizer, the casting speed is increased, the production efficiency is improved, and the product quality is ensured.
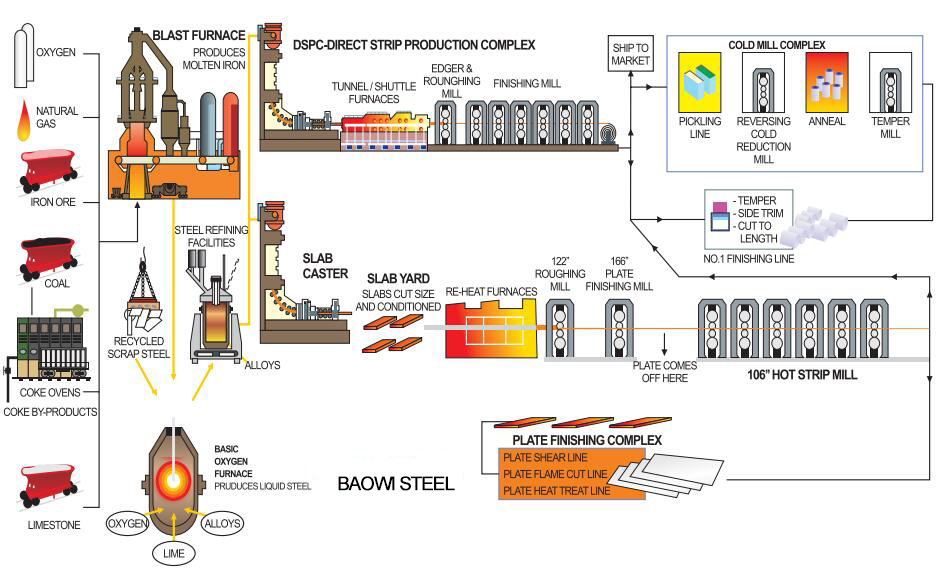
Steel production process: from raw materials to finished products
Steel production begins with iron ore, a raw material widely distributed in many parts of the earth. Many deposits in China are near the surface and easy to mine. The iron ore mined from various places is transported to the steel mills at the destination, where it is unloaded and stored by large cranes in preparation for the next production.
At BAOWI Steel, we use modern facilities to transform the ore into high-quality molten iron. We use the traditional blast furnace process, but in the future, we plan to gradually switch to a more environmentally friendly production method, using hydrogen instead of coal to produce iron. This transition requires some transformation of our production equipment. Until the transformation is completed, we will continue to use blast furnaces for iron smelting.
Iron smelting: melting in the blast furnace
In the blast furnace, we melt iron ore at high temperatures to transform it into liquid iron. Iron ore itself contains a sand-like structure, so it cannot be directly put into the blast furnace for smelting. First, we process the iron ore in a sintering plant to burn it into porous blocks called sinter. Fine ore is processed into small balls, called pellets, at the pelletizing plant, which are easy to transport and react effectively with hot coal and hot air.
These sintered ore and pellets are transported to the top of the 80-meter-high blast furnace by elevators and placed into the furnace in neat layers by a batching device. At the bottom of the blast furnace, large amounts of hot air and finely ground coal are blown in continuously, which raises the temperature inside the blast furnace to 2,300°C, at which point the iron ore begins to melt. Once enough hot metal is generated, the blast furnace is opened by drilling holes to release the molten iron. Finally, the hot iron is collected in special train cars and prepared for the next step of steelmaking.
Converter steelmaking: pig iron becomes steel
At BAOWI Steel, our converter plant is responsible for converting pig iron into steel. In the converter, we add oxygen to raise the temperature inside the furnace and add scrap steel to control the temperature so that it does not get too high. The use of scrap steel not only helps us better control the temperature, but also promotes circularity in steel production. Empty cans, old cars, refrigerators and even abandoned bridges can all be repurposed and transformed into new steel products.
Steel is an ideal circular product that can be recycled an unlimited number of times without losing quality. In this way, we not only reduce resource consumption but also the impact on the environment.
Casting and rolling: steel shaping
After steelmaking, the molten steel is cast into billets, which are then processed into coils of different thicknesses through hot and cold rolling processes. BAOWI Steel's rolling process enables the production of many types of steel according to customer needs, including ultra-strong steel for cars or thin steel sheets for food packaging. During the rolling process, the crystal structure of the steel changes, giving the product the required strength, toughness and other properties.
After rolling, the steel is coated with a thin layer of tin, paint, zinc or plastic, depending on the application. This increases the corrosion resistance of the steel and extends its service life. After all processing is completed, the steel is strictly packaged to ensure that it is not damaged during transportation and is finally delivered to manufacturers in various industries.
Application areas: Steel is everywhere
The steel produced by
BAOWI Steel is widely used in construction, automobiles, home appliances, industrial equipment and food packaging. Whether it is construction steel bars, high-strength steel used in automobile bodies, or thin steel sheets used in canned packaging, BAOWI Steel provides high-quality steel products to meet the needs of various industries.








 English
English Español
Español بالعربية
بالعربية











 Phone :
Phone :  Whatsapp :
Whatsapp :  Email :
Email : 


