Introduction to the production process of hot-rolled steel pipes
Hot-rolled steel pipes are a common steel pipe material. Their production process is mainly processed at high temperatures. They have high toughness and oxidation resistance and are widely used in many fields such as construction, mechanical equipment, and fluid transportation. Compared with cold-rolled steel pipes, the production process of hot-rolled steel pipes is simpler and suitable for most steel pipe production. Below we will introduce the production process of hot-rolled steel pipes in detail.
1. The main process of hot-rolled steel pipe production
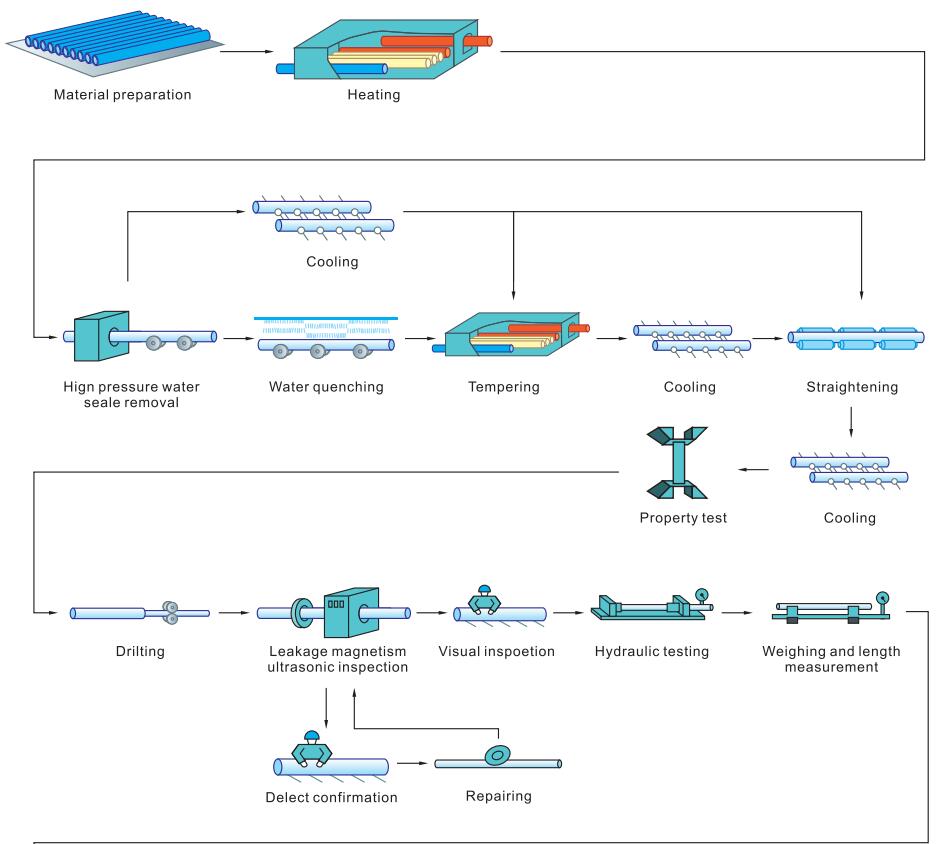
The production process of hot-rolled seamless steel pipes includes several key steps, each of which has an important impact on the quality of the final product. The specific steps are as follows:
Pipe blank preparation and inspection: First, it is necessary to prepare the pipe blank (that is, the initial form of the steel pipe) and conduct a quality inspection to ensure that it meets the production requirements.
Pipe blank heating: The pipe blank is heated to a certain temperature in a heating furnace, usually 1000-1200℃, to soften it and facilitate subsequent processing.
Piercing: After the pipe blank is heated, a perforation process is used to pierce the center of the pipe blank through a series of mechanical equipment to form a hollow rough pipe.
Pipe rolling: The rough pipe after perforation will enter the pipe rolling unit and be rolled multiple times at high temperature to gradually stretch it into the required outer diameter and wall thickness.
Steel pipe reheating: At this time, the steel pipe has been roughly rolled out, but in order to ensure its size and surface quality, it needs to be heated again.
Sizing (reducing): The steel pipe after reheating will be sized or reduced to ensure that its outer diameter and wall thickness meet the standard requirements.
Heat treatment: At this stage, the steel pipe will undergo heat treatment processes such as normalizing or annealing to improve its mechanical properties and processing properties.
Finished pipe straightening: Straighten the formed steel pipe to remove possible bends or deformations and ensure the straightness of the steel pipe.
Finishing: Including removing burrs, cutting and trimming the size of the steel pipe to meet the technical requirements.
Inspection: The steel pipe is inspected for quality through non-destructive testing, physical and chemical testing, etc. to ensure that it meets the product standards.
Warehousing: Finally, the qualified steel pipes will be marked with specifications and put into storage, waiting for shipment.
2. Comparison between hot-rolled seamless steel pipe and cold-rolled seamless steel pipe
Hot-rolled seamless steel pipe and cold-rolled seamless steel pipe differ in production process and product characteristics. The production process of cold-rolled seamless steel pipe is usually more complicated than hot-rolled, and the required technology and equipment are also more precise. The specific differences are as follows:
Production process: Cold-rolled seamless steel pipe needs to go through multiple processes such as pickling, cold rolling, annealing, etc., while hot-rolled seamless steel pipe is processed at high temperature and does not require complex cold processing.
Dimensional accuracy: The dimensional accuracy of cold-rolled seamless steel pipe is higher, usually more accurate than hot-rolled seamless steel pipe.
Surface quality: The surface of cold-rolled seamless steel pipe is smoother and the surface roughness is lower, which is suitable for occasions requiring high surface quality.
3. Application of hot-rolled steel pipe
Hot-rolled steel pipe is widely used in many fields due to its high toughness and good processability:
Construction engineering: Hot-rolled steel pipe is usually used for infrastructure construction such as water pipes and heating pipes in construction.
Mechanical equipment: Used to manufacture mechanical parts, especially parts in large-scale mechanical equipment that have high strength requirements for steel pipes.
Fluid transportation: Hot-rolled steel pipes are often used in fluid transportation pipelines, such as the transportation of oil, natural gas, chemicals, etc.
4. Specifications and materials of hot-rolled steel pipes
The specifications of hot-rolled steel pipes are usually expressed by outer diameter and wall thickness. For example, the outer diameter is greater than 32mm and the wall thickness can reach 200mm. Common materials include high-quality carbon steel, low-alloy structural steel, etc. Common materials such as 10, 20, 45, 40Cr, etc. are used to manufacture various types of pipes and mechanical parts.
Hot-rolled steel pipes have strong oxidation resistance and high toughness, and are suitable for the construction of various large-scale projects and fluid transportation pipelines. Its production process is relatively simple and suitable for large-scale production. In the application of construction engineering, machinery manufacturing and other fields, hot-rolled steel pipes play an important role. Therefore, understanding the production process and characteristics of hot-rolled steel pipes is crucial for engineering applications and steel pipe procurement.









 English
English Español
Español بالعربية
بالعربية












 Phone :
Phone :  Whatsapp :
Whatsapp :  Email :
Email : 


