-
Company Profile
Company Profile
Factory View
Corporate Culture
Warehouse
Organization Chart
-
Research & Development
Technology Patent
R&D Center
Equipment
-
Investor Relations
Business Ethics Policy
Investor Relations
-
Careers
Employee Promotion
Recruitment
Benfits
-
1st Steel Pipe Manufacturing Base

Carbon Steel Pipe
ERW Steel Pipe
LSAW Steel Pipe
SSAW Steel Pipe
Seamless Steel Pipe
Ductile Iron Pipe
-
2nd Steel Pipe Manufacturing Base

Stainless Steel Pipe
Stainless Seamless Steel Pipe
Stainless Welded Steel Pipe
-
3rd Steel Pipe Manufacturing Base

Hollow Section
Square Tube
Rectangular Tube
Rebar
Steel Round Bar
-
OCTG Manufacturing Base

Octg Products
Casing and Tubing
Drill Pipe
Drill Collar
Pup Joints
Slotted Casing
Screen Casing
-
Fittings Manufacturing Base

Pipe Fittings
Flange
Valves
Elbow
Reducer
Tee
-
Metal Pipe Manufacturing Base

Metal Pipe
Copper Pipe
Aluminum Pipe
-
Processed Products Manufacturing Base

Processed Products
Flanged Pipe
Grooved Pipe
-
Services
Pipe Threading
Pipe Beveling
Pipe Coating
Cut and Roll Grooving
Pipe Cutting
Shot Blasting
-
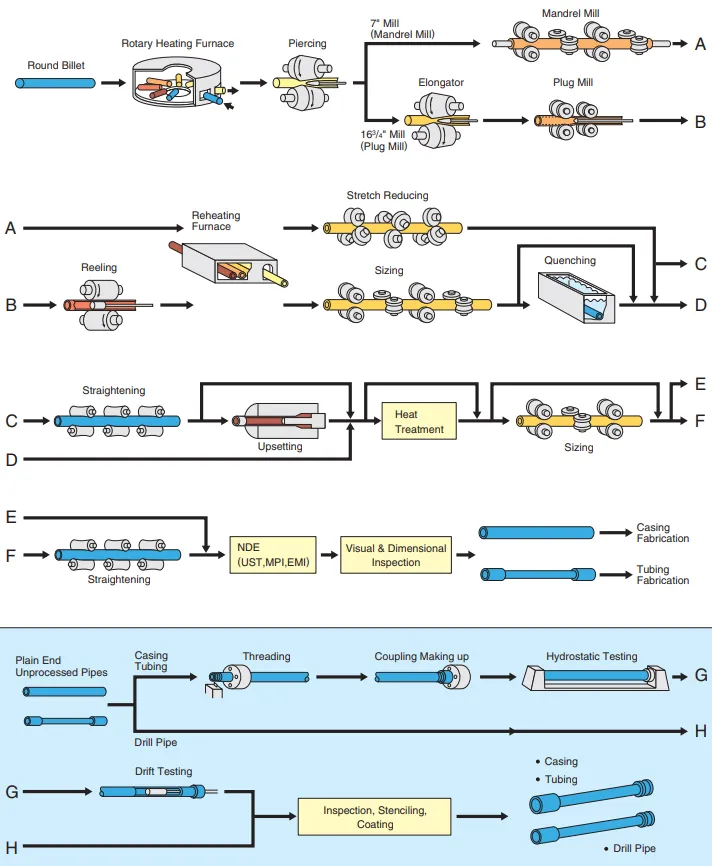
Process
Steel Making Process
Tube Manufacturing Process
Heat Treatment Process
Tube Finishing Process
Coating Process
-
Projects
National Projects
Domestic Projects
Financing Projects
-
Business Scope
Steel Manufacturing
International Trade
Architecture services
-
Qualtiy Control
Inspection
Pipe Transport

 English
English Español
Español بالعربية
بالعربية

















 Phone :
Phone :  Whatsapp :
Whatsapp :  Email :
Email : 


