ASTM A178 and ASME SA-178 are standard specifications for electric-resistance-welded (
ERW steel pipe) carbon steel and carbon-manganese steel pipes. These pipes are primarily used in high-pressure boilers, boiler flues, superheater flues, and safe ends. ASTM A178 specifies three grades of steel pipes: Grade A (low carbon steel), Grade C (medium carbon steel), and Grade D (carbon-manganese steel). This article will provide a detailed introduction to ASTM A178 ERW steel pipes, covering their specifications, manufacturing process, heat treatment, testing and inspection methods, and specific applications.
Specifications and Sizes of ASTM A178 ERW Steel Pipes
ASTM A178 covers a wide range of pipe sizes and thicknesses. Generally, these pipes have an outer diameter ranging from 1/2" to 5" (12.7 mm to 127 mm) and a wall thickness ranging from 0.035" to 0.320" (0.9 mm to 8.1 mm). These specifications allow ASTM A178 ERW steel pipes to be suitable for various high-pressure boiler and superheater applications. Furthermore, although the standard specifies certain sizes, pipes with other dimensions can be provided as long as they meet all other requirements of ASTM A178/ASME SA-178.
Materials and Grades of ASTM A178 ERW Steel Pipes
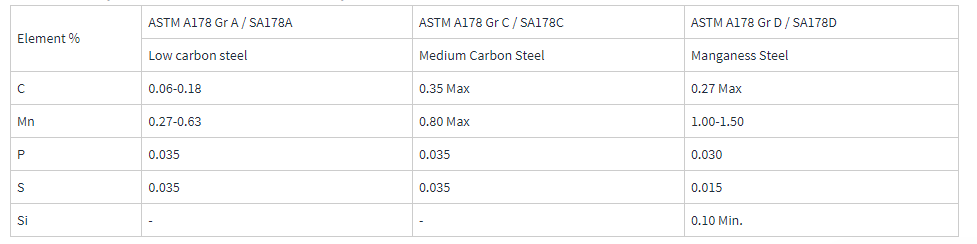
ASTM A178 ERW steel pipes are classified into three grades based on their carbon and manganese content:
Grade A (low carbon steel): Contains lower carbon content, offering good weldability and suitability for low to moderate temperature applications.
Grade C (medium carbon steel): Contains medium carbon content, providing higher strength and hardness, suitable for moderate to high temperature applications.
Grade D (carbon-manganese steel): Contains manganese, offering higher strength and wear resistance, suitable for high temperature and high pressure applications.

Manufacturing Process of ASTM A178 ERW Steel Pipes
ASTM A178 steel pipes are manufactured using the electric-resistance-welding (ERW) process. The following steps outline the manufacturing process of ERW steel pipes:
Material Preparation: Hot-rolled coils or slit coils are used as raw materials. All incoming coils are verified for their chemical and mechanical properties based on test certificates provided by the steel mill.
Forming: ERW steel pipes are cold-formed into cylindrical shapes from steel plates or strips. Unlike hot-forming, the cold-forming process ensures the dimensional accuracy and consistency of the pipes.
Welding: Instead of using flames, the edges of the strip are heated using electric current for welding. This welding process does not require filler metal; instead, welding pressure causes some metal to extrude from the joint, forming metal beads on the inside and outside of the pipe. During welding, these beads or weld flash are trimmed or completely removed.
Heat Treatment: After welding, all pipes must undergo heat treatment at a temperature of at least 1650°F (900°C) and then be cooled in air or in a controlled atmosphere furnace. For cold-drawn pipes, they must be heat-treated at 1200°F (650°C) or higher after the final cold-drawing pass.
Heat Treatment of ASTM A178 ERW Steel Pipes
Heat treatment is a crucial step in the manufacturing of ASTM A178 ERW steel pipes, ensuring the pipes have excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The specific heat treatment processes are as follows:
Post-Weld Heat Treatment: All pipes must undergo heat treatment at a minimum temperature of 1650°F (900°C) after welding, followed by cooling in air or a controlled atmosphere furnace. This process helps to eliminate internal stresses induced during welding, enhancing the mechanical properties of the pipes.
Post-Cold-Draw Heat Treatment: For cold-drawn pipes, they must undergo heat treatment at a temperature of 1200°F (650°C) or higher after the final cold-drawing pass. This process ensures that the deformation stresses induced during cold drawing are effectively relieved, improving the overall performance of the pipes.
Testing and Inspection of ASTM A178 ERW Steel Pipes
To ensure the quality and reliability of ASTM A178 ERW steel pipes, these pipes must undergo a series of rigorous tests and inspections, including:
Flattening Test: This test evaluates the pipe's ability to withstand external pressure without significant deformation, ensuring its safety and reliability in actual applications.
Flange Test: This test checks the sealing performance and mechanical strength of the pipe at the flange connection, ensuring its sealing effectiveness under high pressure.
Tensile Test: This test measures the tensile strength and elongation of the pipe, assessing its load-bearing capacity in high-temperature and high-pressure environments.
Reverse Flattening Test: This test evaluates the pipe's ability to withstand reverse tensile forces, ensuring its stability in complex stress environments.
Hydrostatic Test: This test subjects the pipe to high-pressure water to evaluate its pressure resistance, ensuring its reliability under high pressure.
Nondestructive Electrical Test: This test uses nondestructive methods to inspect the pipe for internal defects, ensuring the integrity of its internal structure.
Dimensional Inspection: This test involves precise measurement of the pipe's dimensions to ensure compliance with the standard specifications.
Visual Inspection: This test inspects the surface quality of the pipe, ensuring it is free from visible defects.
Ultrasonic Inspection: This test uses ultrasonic technology to examine the internal structure and welding quality of the pipe, ensuring it is free from internal defects.
Applications of ASTM A178 ERW Steel Pipes
ASTM A178 ERW steel pipes are widely used in various high-temperature and high-pressure environments, particularly in boilers and superheaters. Specific application areas include:
Power Industry: Used in power boilers and superheaters to transport high-temperature and high-pressure steam and water, ensuring the efficient operation of power equipment.
Petrochemical Industry: Used in boilers and heating equipment of petrochemical plants to transport high-temperature and high-pressure gases and liquids, ensuring the safety and stability of the petrochemical production process.
Industrial Boilers: Used in various industrial boilers to transport high-temperature and high-pressure steam and water, meeting the heat energy requirements in industrial production processes.
Chemical Composition of ASTM A178 ERW Steel Pipe:
Conclusion
ASTM A178 ERW steel pipes are an ideal choice for boiler and superheater pipes. Their strict manufacturing process and comprehensive testing standards ensure their reliable performance in high-temperature and high-pressure environments. From material selection and manufacturing processes to testing and inspection, the ASTM A178 standard provides detailed guidance to ensure these steel pipes meet the high demands of industrial applications. Through this detailed analysis, we hope to help readers better understand all aspects of ASTM A178 ERW steel pipes and provide a reference for practical applications.








 English
English Español
Español بالعربية
بالعربية












 Phone :
Phone :  Whatsapp :
Whatsapp :  Email :
Email : 


