Casing Coupling vs. Tubing Coupling: Key Differences and How to Choose
In the oil and gas industry, casing couplings and tubing couplings play essential roles in wellbore integrity and production efficiency. Understanding their differences and selecting the right coupling type can improve well performance and reduce operational risks. This guide compares casing couplings and tubing couplings, covering specifications, applications, and key selection factors.
Casing pipe is an insulating device that introduces live conductors into electrical equipment or passes through walls. The former is called an electrical casing, and the latter is called a wall casing. The casing structure generally consists of three parts: a conductor (guide rod), an insulator, and a metal flange. The conductor passes through the axis of the cylindrical insulator, and the metal annular flange is installed outside the insulator and used for grounding. The casing is an insulating structure with a strong vertical electric field component. The electric field intensity at the metal flange is very large, which is prone to corona discharge and flash discharge along the surface of the medium. The radial electric field intensity between the flange and the guide rod is also very high, which is prone to breakdown of the insulating medium. In addition to the use of a single solid insulating material for casings of 35kV and below, multiple insulating materials are often used or electric field uniformity measures are taken to make the axial and tangential electric field distribution tend to be uniform.
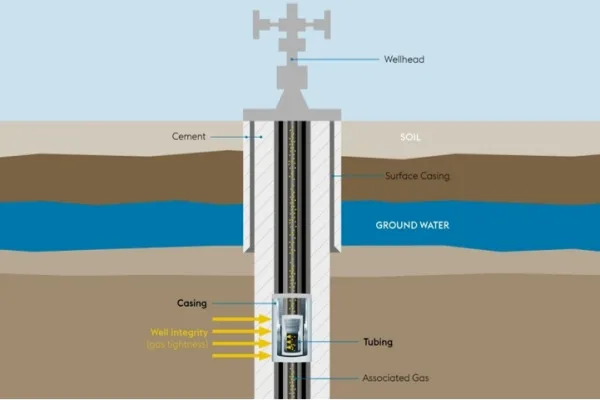
What Is a Casing Coupling?
A casing coupling is a short pipe used to connect two casing joints in oil and gas wells. Casing provides structural support and protects the wellbore from collapse and external pressures. These couplings are manufactured according to API 5CT casing coupling standards to ensure reliability in drilling operations.
Types of Casing Couplings
BTC (Buttress Thread Coupling): Designed for high-pressure applications with superior sealing performance.
LTC (Long Thread Coupling): Features longer threads for enhanced connection strength.
STC (Short Thread Coupling): Easier to install but provides lower tensile strength.
Definition of Tubing Coupling
A tubing coupling connects tubing joints, which transport oil, gas, or fluids from the wellbore to the surface. These couplings must withstand internal pressure and fluid flow while maintaining a secure seal. Like casing couplings, tubing couplings adhere to API 5CT tubing coupling standards.
Types of Tubing Couplings
EUE (External Upset End) Tubing Coupling: Provides better strength and fatigue resistance.
NUE (Non-Upset End) Tubing Coupling: Has a thinner profile, allowing for a more compact connection.
Key Differences Between Casing and Tubing Couplings
1. Different structures: The Casing nipple is installed on the casing pipe , while the coupling is installed on the outside of the pipe. The structure of the casing coupling mainly consists of two parts, namely the casing of the pipe and the connecting pipe. The casing pipe is generally cylindrical, with a larger inner diameter and a smaller outer diameter, which is convenient for casing s on pipes with smaller outer diameters; the connecting pipe is generally a flat ring, which is used to connect the casing pipe and the pipe with a larger outer diameter.
2. Different manufacturing processes: The casing nipple needs to be threaded on the casing pipe , then a hole is opened on the casing pipe, and finally fixed with a joint. The coupling needs to fold a piece of steel plate, then weld the steel plates together, and then process it into a semicircle, and finally fix it on the outside of the pipe with bolts.
3. Different application scenarios: The casing nipple is mainly used for pipeline connections in the fields of petroleum, chemical industry, natural gas and construction, while the casing coupling is mainly used for pipeline connections in general industries.
4. Type: The types of casing joints include plug-type casing heads, inner cone-type casing heads, outer cone-type casing heads, and cone-hole casing heads; there are many types of casing couplings, mainly including cast iron casing joints, steel casing joints, and stainless steel casing joints. According to the different connecting pipes, casing couplings are also divided into bayonet casing joints and flange casing joints.
|
Feature
|
Casing Coupling
|
Tubing Coupling
|
|
Function
|
Supports and protects the well structure
|
Transports fluids from the wellbore to the surface
|
|
Size Range
|
Larger diameters (4.5" - 20"+)
|
Smaller diameters (1.05" - 4.5")
|
|
Thread Type
|
BTC, LTC, STC
|
EUE, NUE
|
|
Pressure Handling
|
External pressure resistance
|
Internal pressure resistance
|
|
Application
|
Well casing support
|
Oil and gas production
|
How to Choose Between Casing and Tubing Couplings
Choosing the right coupling depends on several factors:
1. Well Design Requirements
If you need to maintain structural integrity, go with casing couplings.
If the goal is fluid transport, select tubing couplings.
2. Pressure and Load Conditions
High-pressure environments require BTC casing couplings or EUE tubing couplings for added durability.
For standard applications, STC or NUE couplings may be sufficient.
3. Material Selection for Corrosion Resistance
In CO₂ or H₂S-rich environments, use alloy steel casing couplings or corrosion-resistant tubing couplings.
For general applications, carbon steel tubing couplings offer a cost-effective solution.
Industry Standards for Casing and Tubing Couplings
Both coupling types must meet
API 5CT standards, which specify dimensions, material grades, and connection performance. Well operators should always verify that their couplings are ISO-certified tubing couplings to ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Summarize
Understanding the differences between casing couplings and tubing couplings is critical for well integrity and production efficiency. Selecting the correct coupling type based on well conditions, pressure, and corrosion resistance ensures long-term performance and cost savings. Always choose API and ISO-certified couplings to maintain reliability in oilfield operations.By optimizing your selection process, you can enhance well safety, reduce maintenance costs, and improve overall production efficiency.
BAOWI STEEL provides high-quality API 5CT casing and tubing couplings with premium materials, global supply, and competitive pricing—ensuring reliability for your oil and gas projects.








 English
English Español
Español بالعربية
بالعربية











 Phone :
Phone :  Whatsapp :
Whatsapp :  Email :
Email : 


