By definition, a
valve is a device that controls the flow of fluids.Specifically, it is a mechanical device designed to direct, start, stop, mix or regulate the flow, pressure or temperature of a process fluid. The "fluid" handled by the valve may be air, water, steam, corrosive chemicals, mud, oil, gas, liquid metal, powder, slag or other dry materials, etc. By driving its closing member to move up and down, slide, rotate or swing, the valve can change its flow area to control the flow of fluids.
Valves are widely used in various pipeline and pipe applications such as oil and gas industry, chemical industry, power plants, pulp and paper, food and beverage, nuclear energy, offshore and marine, aerospace and aviation, water supply, sewage treatment and other civil engineering. Different valves can be suitable for working pressure ranges from 1.3 x 10⁻³ MPa to 1000 MPa, and working temperature ranges from -269°C to 1430°C.
Basic Working Principle of Valves
At its core, the working principle of a valve revolves around a movable component—such as a disc, ball, gate, or diaphragm—that alters the passage of fluid through the valve body. When the actuator (manual handwheel, electric motor, pneumatic piston, or hydraulic cylinder) is engaged, it moves the internal mechanism to either block, allow, or throttle flow. This movement is aligned with the valve’s specific design type, such as linear motion or rotary motion.
For example:
Gate valves operate by lifting a gate out of the fluid path for full flow and lowering it to shut off flow.
Ball valves use a rotating ball with a bore to control flow with a quarter-turn action.
Butterfly valves rely on a disc that rotates to open or close the fluid passage.
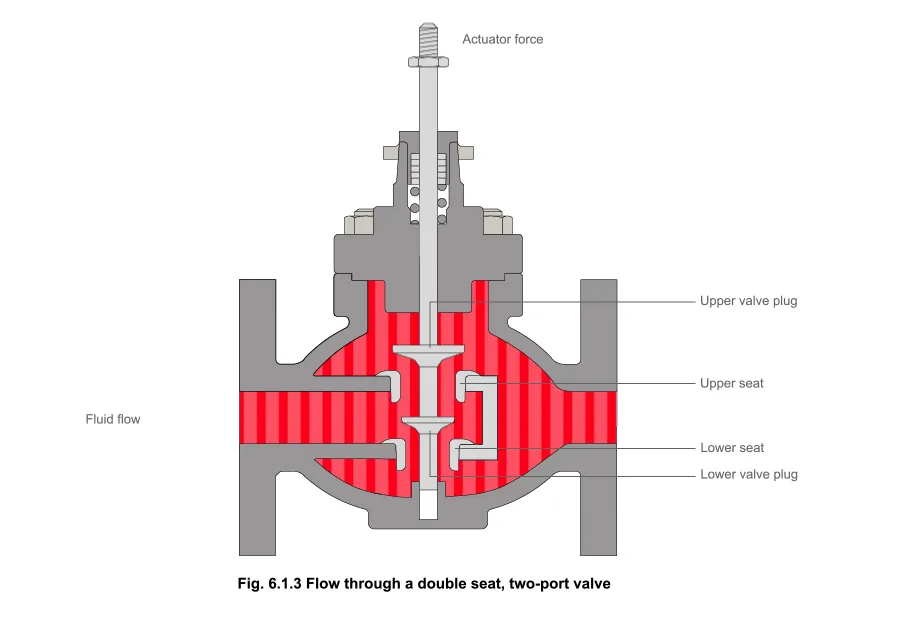
Globe valves use a plug that moves up and down to regulate flow, ideal for throttling.
1. Valves are pipe accessories used to open and close pipelines, control flow direction, and adjust and control the parameters (temperature, pressure, and flow) of the conveying medium. According to their functions, they can be divided into shut-off valves, check valves, regulating valves, etc.
2. The control of valves can adopt a variety of transmission methods, such as manual, electric, hydraulic, pneumatic, turbine, electromagnetic, electromagnetic hydraulic, electro-hydraulic, gas-hydraulic, spur gear, bevel gear drive, etc.; they can act according to predetermined requirements under the action of pressure, temperature or other forms of sensor signals, or simply open or close without relying on sensor signals. The valve relies on the drive or automatic mechanism to make the opening and closing parts move up and down, slide, swing or rotate, thereby changing the size of its flow area to achieve its control function.
Valve structure principle
The sealing performance of the valve refers to the ability of each sealing part of the valve to prevent the leakage of the medium. It is the most important technical performance indicator of the valve. There are three sealing parts of the valve: the contact between the opening and closing parts and the two sealing surfaces of the valve seat; the matching part between the packing and the valve stem and the stuffing box; the connection between the valve body and the valve cover. The leakage of the first one is called internal leakage, which is usually called loose closure. It will affect the ability of the valve to cut off the medium. For cut-off valves, internal leakage is not allowed. The leakage of the last two parts is called external leakage, that is, the medium leaks from the inside of the valve to the outside of the valve. External leakage will cause material loss, pollute the environment, and cause accidents in serious cases. For flammable, explosive, toxic or radioactive media, external leakage is even more unacceptable, so the valve must have reliable sealing performance.
Types of Valves and Their Functions
Each valve type is designed with a specific function and working principle to suit various application needs:
|
Valve Type
|
Working Principle Description
|
Common Application Areas
|
|
Ball Valve
|
90° rotation of a hollow ball to open or close flow
|
Water supply, oil & gas pipelines, HVAC
|
|
Gate Valve
|
Vertical movement of a flat gate to control full on/off flow
|
Municipal water lines, fire protection systems
|
|
Butterfly Valve
|
Rotating disc on a central axis to throttle or stop flow
|
Chemical plants, wastewater treatment
|
|
Globe Valve
|
Linear motion plug for precise throttling of flow
|
Steam systems, cooling circuits
|
|
Check Valve
|
Allows flow in one direction and prevents backflow (self-actuated)
|
Pump outlets, chemical lines
|
|
Diaphragm Valve
|
Flexible diaphragm pressed onto a seat to stop or release flow
|
Food-grade and pharmaceutical systems
|
How to Use Valves Correctly: Essential Tips for Safe Operation
1.Valves are essential components in any piping system, controlling the flow of liquids, gases, or steam. Incorrect use can lead to leakage, system failure, or safety hazards. Here’s how to use them properly:
2.Choose the Right Valve: Select based on the medium (water, steam, corrosive fluids) and pressure/temperature requirements. Use materials like stainless steel, carbon steel, or PVC accordingly.
3.Install with Care: Always follow the flow direction indicated on the valve body. Clean the pipe before installation to avoid internal damage.
4.Operate Gently: Open and close valves slowly to prevent water hammer. Use gate valves only for full open/close—not for throttling.
5.Maintain Regularly: Inspect for leaks, lubricate moving parts, and keep the valve area clean to prevent corrosion.
6.Avoid Common Mistakes: Don’t overtighten handles, weld near closed valves, or use the wrong valve type for your application.
Valve Manufacturers and Suppliers
At Baowi Steel, we supply high-quality industrial valves for oil, gas, water, and chemical applications. As a trusted valve manufacturer and global supplier, our products are engineered for durability, reliability, and performance under extreme conditions. Whether you need standard gate valves or custom-built solutions, Baowi Steel delivers precision and excellence at scale.








 English
English Español
Español بالعربية
بالعربية











 Phone :
Phone :  Whatsapp :
Whatsapp :  Email :
Email : 


