You may have heard of Schedule 40 pipe in your home improvement or engineering projects. It is actually one of the most common pipe specifications. To make your pipe system safe and efficient, it is important to know how much pressure it can withstand. This article will explain the pressure rating of Schedule 40 pipe in a simple and clear way, tell you how to determine the pressure strength, and provide detailed charts of various materials to help you easily choose the right pipe, whether you are an engineer, construction worker, or DIY enthusiast.
To ensure clear and consistent construction, ASME B36.10 regulates the dimensions of wrought steel pipe, and ASME B36.19 does the same for stainless steel pipe. Detailed tables provide size and weight information for Schedule 40 pipe to help with precise installation. The pipe number is a key factor in determining the pressure resistance and pressure resistance of the pipe. The pressure rating formula is SCH * P = S (where SCH is the pipe number, P is the maximum internal pressure, and S is the allowable stress), which provides a systematic way to evaluate pressure resistance.
Schedule 40 pipes are widely used because they offer sufficient strength for many applications at a relatively affordable cost. They are manufactured in various materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, PVC, and galvanized steel, each with distinct pressure handling capabilities.
Advanced Pressure Rating Calculations
Calculating pressure ratings requires the use of a modified Barlow formula that accounts for factors such as pipe wall thickness, outside diameter, allowable pressure, stresses, longitudinal joint quality, and wall thickness corrections. Calculating pressure ratings requires the use of a modified Barlow formula that accounts for factors such as pipe wall thickness, outside diameter, allowable pressure, stresses, longitudinal joint quality, and wall thickness corrections. Calculating pressure ratings requires the use of a modified Barlow formula that accounts for factors such as pipe wall thickness, outside diameter, allowable pressure, stresses, longitudinal joint quality, and wall thickness corrections. This advanced approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of the pressure capabilities of the pipeline.
Factors that affect pressure levels of Schedule 40 Pipe
The pressure rating of a pipe is the maximum internal pressure it can safely withstand at a given temperature without failure. Pressure ratings are influenced by:
Material Type: Different materials have different strength and temperature tolerances.
Wall Thickness: Thicker walls can handle higher pressure.
Pipe Diameter: Larger diameters usually reduce pressure capacity.
Operating Temperature: Higher temperatures generally decrease pressure ratings.
Manufacturing Standards: Compliance with API, ASTM, or ASME standards affects reliability.
Schedule 40 is a wall thickness designation, not a direct pressure rating. Therefore, pressure ratings for Schedule 40 pipes vary by material and size.
Schedule 40 Pipes Pressure Rating Chart
The following table presents the Maximum Allowable Pressure (also known as pressure rating) for Schedule 40 pipes across a range of nominal pipe sizes (NPS). The pressure values are shown in psi (pounds per square inch) and kPa (kilopascal), reflecting common units used globally.
|
Maximum Allowable Pressure (psi) (kPa)
|
|
NPS
|
Outside Diameter
|
Schedule
|
|
(inch)
|
(inch)
|
40
|
|
(mm)
|
|
1/4 inch
|
0.54 inch
|
7985
|
|
13.7 mm
|
55057
|
|
3/8 inch
|
0.675 inch
|
6606
|
|
17.1 mm
|
45548
|
|
1/2 inch
|
0.84 inch
|
6358
|
|
21.3 mm
|
43838
|
|
3/4 inch
|
1.05 inch
|
5273
|
|
26.7 mm
|
36357
|
|
1 inch
|
1.315 inch
|
4956
|
|
33.4 mm
|
34172
|
|
1 1/4 inch
|
1.66 inch
|
4133
|
|
42.2 mm
|
28497
|
|
1 1/2 inch
|
1.9 inch
|
3739
|
|
48.3 mm
|
25780
|
|
2 inch
|
2.375 inch
|
3177
|
|
60.3 mm
|
21905
|
|
2 1/2 inch
|
2.875 inch
|
3460
|
|
73 mm
|
23857
|
|
3 inch
|
3.5 inch
|
3024
|
|
88.9 mm
|
20850
|
|
3 1/2 inch
|
4 inch
|
2769
|
|
102 mm
|
19092
|
|
4 inch
|
4.5 inch
|
2581
|
|
114 mm
|
17796
|
|
5 inch
|
5.563 inch
|
2273
|
|
141 mm
|
15672
|
|
6 inch
|
6.625 inch
|
2071
|
|
168 mm
|
14280
|
|
8 inch
|
8.625 inch
|
1829
|
|
219 mm
|
12611
|
|
10 inch
|
10.75 inch
|
1664
|
|
273 mm
|
11473
|
|
12 inch
|
12.75 inch
|
1560
|
|
324 mm
|
10756
|
|
14 inch
|
14 inch
|
1533
|
|
356 mm
|
10570
|
|
16 inch
|
16 inch
|
1531
|
|
406 mm
|
10556
|
|
18 inch
|
18 inch
|
1530
|
|
457 mm
|
10549
|
|
20 inch
|
20 inch
|
1455
|
|
508 mm
|
10032
|
|
22 inch
|
22 inch
|
|
|
559 mm
|
|
24 inch
|
24 inch
|
1405
|
|
610 mm
|
9687
|
|
30 inch
|
30 inch
|
|
|
762 mm
|
|
32 inch
|
32 inch
|
1054
|
|
813 mm
|
7267
|
|
34 inch
|
34 inch
|
992
|
|
864 mm
|
6840
|
|
36 inch
|
36 inch
|
1021
|
|
914 mm
|
7040
|
|
42 inch
|
42 inch
|
875
|
|
1067 mm
|
6033
|
1 in (inch) = 25.4 mm
1 psi (lb/in2) = 6,894.8 Pa (N/m2) = 6.895x10-2 bar
How to Calculate Pressure Rating for Schedule 40 Pipes?
The pressure rating can be estimated using the Barlow's formula:
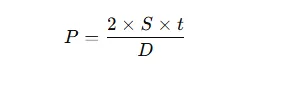
Where:
-
P = Maximum allowable pressure (psi)
-
S= Material allowable stress (psi)
-
t = Wall thickness (inch)
-
D = Outside diameter (inch)
This formula shows why thicker pipes and stronger materials have higher pressure ratings.
PVC Schedule 40 Pipes
PVC pipes are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, commonly used in residential and commercial plumbing. Pressure ratings at 73°F (23°C) are as follows:
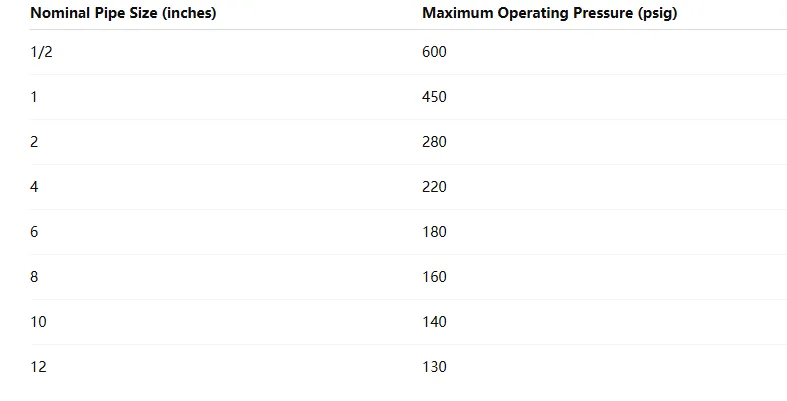
Note: PVC pressure ratings decrease with increasing temperature. For instance, at 110°F (43°C), the pressure rating may reduce to approximately 51% of its value at 73°F (23°C).
Conclusion
Understanding the pressure ratings of
Schedule 40 pipes across different materials is essential for selecting the appropriate piping for your application. Always consider factors such as operating temperature, material properties, and applicable standards. For high-pressure or high-temperature applications, materials like carbon steel or stainless steel may be more suitable, while PVC is ideal for lower-pressure, corrosion-resistant needs.









 English
English Español
Español بالعربية
بالعربية











 Phone :
Phone :  Whatsapp :
Whatsapp :  Email :
Email : 


