Do you know what schedule stands for?
First of all, the word schedule stands for the wall thickness of a pipe, sometimes referred to by the acronym sch. It’s a way of categorizing the wall thickness of a pipe that was developed by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), and the larger the number after the schedule, the thicker the pipe’s walls are and the more pressure it can withstand.
Schedule 40 Pipe Pressure Rating refers to the maximum internal pressure that a Schedule 40 pipe can safely withstand under specific temperature and operating conditions. Because Schedule 40 represents a standard wall thickness, its pressure capacity varies by pipe size, material type, and design standards such as ASTM, ASME, or API.
How Do Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 Pipes Differ in Pressure Rating?
The main difference between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 lies in their wall thickness: Schedule 80 has a thicker wall than Schedule 40, allowing it to withstand higher pressure and temperature, resulting in greater strength. However, it also has a smaller inner diameter, lower flow rate, greater weight, and higher cost. Schedule 40, on the other hand, has a standard wall thickness and is suitable for everyday water pipes, general operating conditions, and low to medium pressure systems. In short: Schedule 40 = standard pressure; Schedule 80 = reinforced pressure-resistant version. All other dimensions (outer diameter) are the same; the only difference is in wall thickness and pressure capacity.
The pipe schedule number is non-dimensional and depends on the nominal pipe size, internal pipe working pressure, and the material used for the pipe wall.The major difference between schedule 40 and schedule 80 pipe is the wall thickness, inside diameter, and their weight.Schedule 80 will have a greater wall thickness, a smaller inside diameter and a higher weight than Schedule 40 pipe at a given nominal pipe size.
SCH 40 vs SCH 80 Steel Pipe Pressure Rating
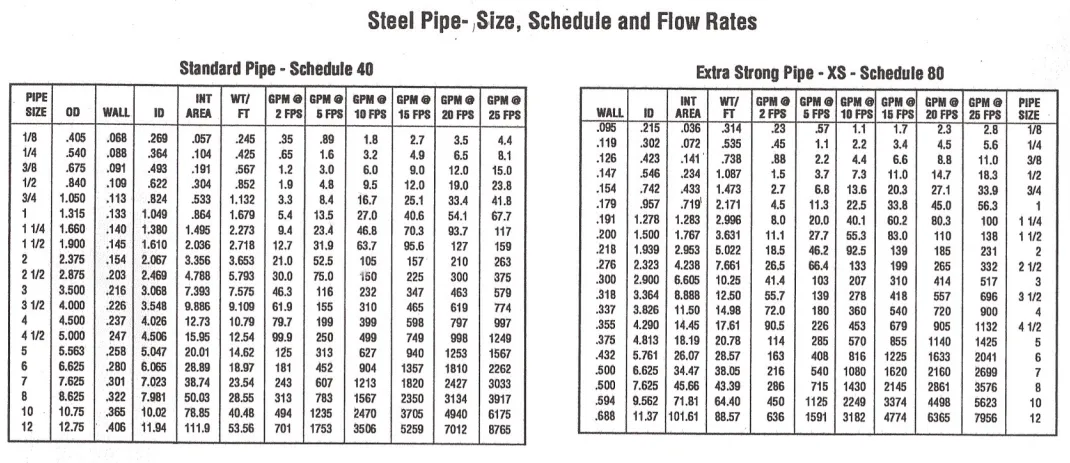
|
Nominal Pipe Size (NPS)
|
Outside Diameter (OD)
|
Schedule 40 Wall Thickness
|
Maximum Pressure (PSI)
|
Schedule 80 Wall Thickness
|
Maximum Pressure (PSI)
|
|
1/8"
|
0.405
|
0.068
|
810
|
0.095
|
1230
|
|
1/4
|
0.540
|
0.088
|
780
|
0.119
|
1130
|
|
3/8
|
0.675
|
0.091
|
620
|
0.126
|
920
|
|
1/2
|
0.840
|
0.109
|
600
|
0.147
|
850
|
|
3/4
|
1.050
|
0.113
|
480
|
0.154
|
690
|
|
1
|
1.315
|
0.133
|
450
|
0.179
|
630
|
|
1 1/4
|
1.660
|
0.140
|
370
|
0.191
|
520
|
|
1 1/2
|
1.900
|
0.145
|
330
|
0.200
|
470
|
|
2
|
2.375
|
0.154
|
280
|
0.218
|
400
|
|
2 1/2
|
2.875
|
0.203
|
300
|
0.276
|
420
|
|
3
|
3.500
|
0.216
|
260
|
0.300
|
370
|
|
3 1/2
|
4.000
|
0.226
|
240
|
0.318
|
350
|
|
4
|
4.500
|
0.237
|
220
|
0.337
|
320
|
|
5
|
5.563
|
0.258
|
190
|
0.375
|
290
|
|
6
|
6.625
|
0.280
|
180
|
0.432
|
280
|
|
8
|
8.625
|
0.322
|
160
|
0.500
|
250
|
|
10
|
10.750
|
0.365
|
140
|
0.593
|
230
|
|
12
|
12.750
|
0.406
|
130
|
0.687
|
230
|
|
14
|
14.000
|
0.437
|
130
|
0.750
|
220
|
|
16
|
16.000
|
0.500
|
130
|
0.843
|
220
|
|
18
|
18.000
|
0.562
|
130
|
0.937
|
220
|
|
20
|
20.000
|
0.593
|
120
|
1.031
|
220
|
|
24
|
24.000
|
0.687
|
120
|
1.218
|
210
|
Summarize
Because Schedule 80 pipes have thicker walls, they can handle higher internal pressure compared to Schedule 40 pipes of the same size.For example, a 1-inch Schedule 40 PVC pipe has a maximum working pressure of about 450 psi, while a 1-inch Schedule 80 PVC pipe can withstand approximately 630 psi.When selecting a pipe, consider the operating pressure of your system. For projects that require higher pressure handling, Schedule 80 PVC is the better option.
In summary, SCH 40 and SCH 80 steel pipes differ primarily in wall thickness, which directly impacts their pressure ratings. While SCH 40 serves most standard applications effectively, SCH 80 provides superior strength and pressure capacity for critical systems. Understanding the interplay of schedule, material, temperature, and application requirements is essential for making informed piping decisions and ensuring long-term reliability.








 English
English Español
Español بالعربية
بالعربية











 Phone :
Phone :  Whatsapp :
Whatsapp :  Email :
Email : 


